Wearing sunscreen is one of the most useful things we can do for our health, yet many of us don't use it properly. Despite repeated public health warnings, there is still some uncertainty about how and when to use sunscreen. Sunburn is responsible for more than 80% of melanoma skin cancer occurrences, thus it's critical to understand how to protect our skin from the sun's dangerous rays.

Why Should We Protect Our Skin from the Sun?
The sun's rays, particularly ultraviolet (UV) radiation, can harm our skin's DNA, proteins, and other molecules. While slight sun exposure helps our skin create vitamin D, too much exposure can cause DNA damage, accelerated aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. UV radiation is the leading cause of the most common types of skin cancer.

Understanding SPF and its importance:
The acronym SPF stands for "sun protection factor." The number next to it represents how much UV radiation is required to create sunburn on protected skin versus unprotected skin. A higher SPF provides additional protection. However, SPF is generally used to assess protection against UVB rays, with UVA protection given by a different grade. The sun's rays are highest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., therefore using sunscreen during these hours is especially essential.

How To Apply Sunscreen Correctly:
Experts recommend that sunscreen be applied 20-30 minutes before sun exposure to allow it to soak into the skin. Applying it twice will assist in covering any missed areas. Reapplication is essential following sweating, swimming, or towel drying. Avoid combining sunscreen with other skincare products, like as moisturizers, as this may decrease its effectiveness.

How do we choose the correct sunscreen?
Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or greater to protect against both UVA and UVB radiation. For longer periods spent outside, look for water-resistant products. When choosing components for sensitive skin, keep your skin type and any sensitivities in mind. Examples include zinc oxide and titanium dioxide. Look for extra qualities such as oil-free or not acne-causing for acne-prone or oily skin types. Choose a product that fits your lifestyle and tastes, whether it's fragrance-free, tinted, or appropriate for daily use.

Sunscreen Expiry and Storage:
Sunscreen gets less effective over time. In general, it is applicable for three years after purchase. Sunscreen should be stored away from direct sunlight and heat to prevent the chemicals from breaking down. Checking for variations in consistency and color might also aid in its effectiveness.
Concerns with sunscreen and vitamin D:
Some people are concerned that sunscreen may interfere with vitamin D production. However, research indicates that the danger of sunscreen altering vitamin D absorption is minimal. The advantages of applying sunscreen to protect against dangerous UV radiation exceed any potential effect on vitamin D levels.
Drawbacks:
While sunscreen is essential for protecting the skin from damaging UV rays, it is not without disadvantages. Some people may have allergic reactions or skin irritation to particular substances. Chemicals in sunscreen, such as oxybenzone, have the potential to alter hormones when absorbed into the body. Furthermore, sunscreen waste in oceans can affect marine life and coral reefs, forcing regulations in certain locations. Focusing entirely on sunscreen may create a false sense of security, resulting in inadequate sun protection measures. Furthermore, sunscreen can inhibit vitamin D absorption, which is essential for bone health and immunity. Despite these concerns, sunscreen's advantages exceed the risks when combined with other sun protection strategies such as seeking cover and wearing protective clothes.
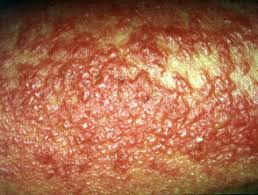
Oxybenzone causes rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, and trouble breathing.
How Much Sunscreen to Use?
The FDA recommends applying around six tablespoons of sunscreen to the face and body of an average adult. According to studies, people often use less than necessary, lowering the level of protection. For children, the dosage changes with age, with smaller children requiring less than older ones. Babies under six months old should not use sunscreen and should be kept out of direct sunlight.
Sunscreen vs Sunblock:
Sunscreen absorbs UV radiation and acts as a chemical barrier, whereas sunblock forms a physical barrier that UV rays cannot penetrate. Both provide great protection, but they must be applied correctly and regularly.
 (2)_1718038304.png)
From April to September, use sunscreen every day and restrict sun exposure, even when using sunscreen. Wearing protective clothing and seeking shade are additional ways to protect your skin. Finally, proper sunscreen application is essential for protecting against the harmful effects of UV radiation. Understanding how to buy, apply, and store sunscreen can help us lower our risk of skin damage and cancer.
Inputs: Agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.





















